
©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC. Copying permitted for educational use.
Visit us at tp4s.com for more SAT and ACT prep materials and to learn about our classes and tutoring services.
The Ultimate Formula Sheet for ACT Math
The ACT does not provide any formulas. Be prepared by making sure to have these ones memorized.
Fractions, Decimals, & Percentages: (for this section, r is the percent in decimal form)
part
Fraction
whole
=
;
100
part
Percent =
Percent Increase or Decrease:
100%
old new
old
−
×
Increase by a percent: multiply by
(1 )r+
Decrease by a percent: multiply by
(1 )r−
Simple Interest:
(1 )A P rt= +
Interest Compounded Annually:
(1 )
t
AP r= +
Interest Compounded n times per year:
1
nt
r
AP
n
= +
Rates, Ratios, & Proportions:
General form of a conversion factor:
_
_
ending units
starting units
Example:
12
10 120
1
inches
feet inches
foot
=
(Concentration of A x Volume of A)
+ (Concentration of B x Volume of B)
= Final concentration (Vol. of A + Vol. of B)
Distance = Rate x Time
Exponents, Roots, & Polynomials:
Multiplication Rule for Exponents:
b c bc
aa a
+
⋅=
Division Rule for Exponents:
b
bc
c
a
a
a
−
=
Power Rule for Exponents:
( )
c
b bc
aa=
Negative Exponents:
1
b
b
a
a
−
=
Fractional Exponents:
( )
b
b
c
b
c
c
a a or a=
1i = −
;
2
1i = −
;
3
ii= −
;
4
1i =
4
1
n
i =
;
41n
ii
+
=
;
42
1
n
i
+
= −
;
43n
ii
+
= −
Complex Conjugates:
( )( )
a bi a bi+−
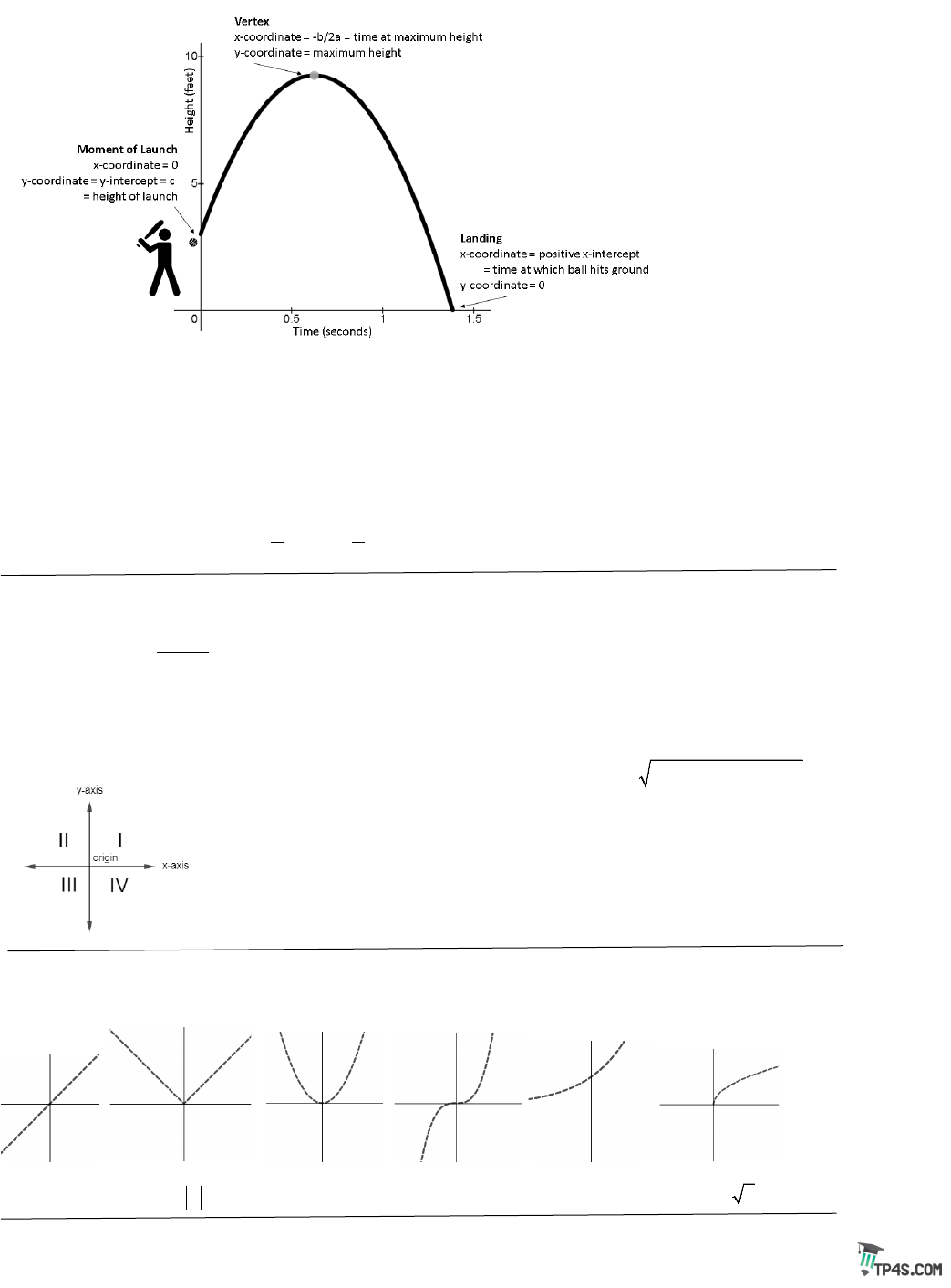
Parabolas:
Standard Form:
2
()f x ax bx c= ++
;
vertex=
,
22
bb
f
aa
−−
;
y-intercept = c;
x-intercepts =
2
4
2
b b ac
a
−± −
Sum of solutions =
b
a
−
Discriminant =
2
4b ac−
; Pos=2 real roots
Zero= 1 real root; Neg=2 imaginary roots
Factored Form:
( ) ( )( )fx axmxn=−−
;
x-intercepts are m and n;
x-coordinate of vertex =
2
mn+
Vertex Form:
2
() ( )fx ax h k
=−+
;
vertex =
(,)hk
The Ultimate Formula Sheet for ACT Math ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC
Difference of Squares:
22
( )( )a b a ba b−=+ −
Sum of Cubes:
33 2 2
( )( )a b a b a ab b+=+ −+
Difference of Cubes:
33 2 2
( )( )a b a b a ab b
−=− ++
Perfect Square Trinomial:
( )
2
22
2a ab b a b+ +=+
and
(
)
2
22
2a ab b a b− +=−
Completing the Square:
22
2
22
bb
x bx x
++ =+
Graphing Lines:
Slope Formula:
21
21
yy
m
xx
−
=
−
Slope of horizontal line = 0
Slope of vertical line = undefined
Standard Form:
Ax By C+=
Slope-Intercept Form:
y mx b= +
Point-Slope Form:
11
()y y mx x−= −
Distance Formula:
22
21 21
( )( )d xx yy
= − +−
Midpoint Formula:
1 21 2
,
22
x xy y
M
++
=
Parallel lines: equal slopes
⊥ Lines: slopes are opposite reciprocals
Parent Graphs & Transformations:
yx=
yx=
2
yx=
3
yx
=
x
ya=
yx=
The Ultimate Formula Sheet for ACT Math ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC
Transformation
Visual effect
()fx k+
Shift up by k units
()fx k−
Shift down by k units
()fx h+
Shift left by h units
()fx h−
Shift right by h units
()fx−
Reflect over the x axis (flip upside down)
()cf x
Stretch vertically by a factor of c (becomes skinnier)
1
()fx
c
Shrink vertically by a factor of c (becomes fatter)
Data & Probability:
__
__
sum of items
Average
number of items
=
Median = center data point
Mode = most frequent data point
Range = maximum – minimum
_
_
desired outcomes
Probability
possible outcomes
=
Probability that independent events A and B will
both happen:
( ) ( ) ()PA B PA PB= ×
Probability that either A or B will happen:
()()()()PA B PA PB PA B=+−
Expected Value:
1
() ( )
n
ii
i
Ex x Px
=
=
∑
Angles:
Vertical ∠’ s are ≅
∠’s that form a linear pair are supplementary (add
up to 180°)
∠’ s that form a circle add up to 360°
When ∥ lines are cut by a transversal, all acute ∠’ s
are ≅ and all obtuse ∠’ s are ≅
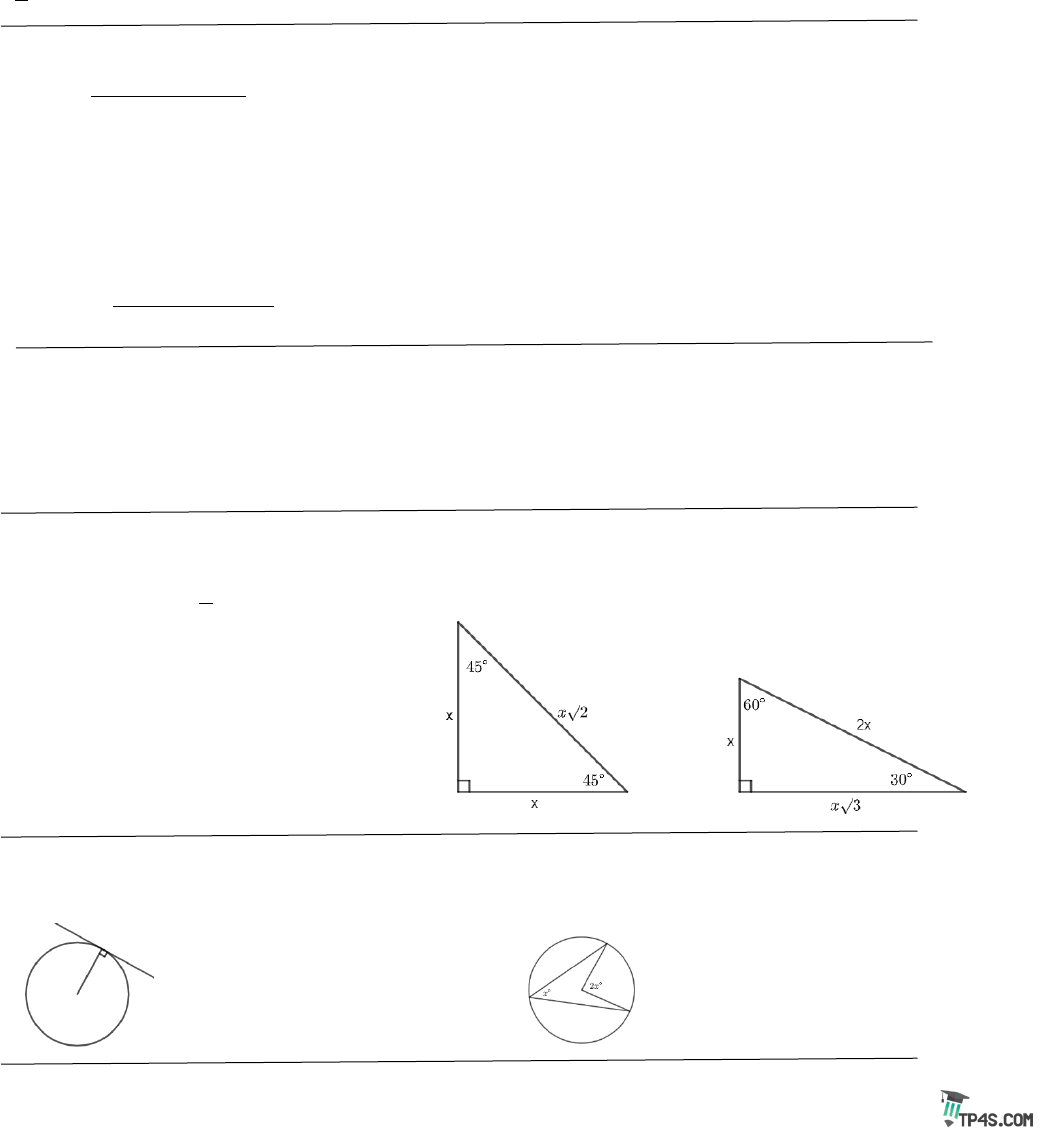
Triangles:
Area of a Triangle:
1
2
A bh=
The three ∠’ s of a ∆ add up to 180°
An exterior ∠ is equal to the sum of the two
remote interior ∠’ s
Pythagorean Theorem:
222
abc+=
Pythagorean Triples: 3-4-5 and 5-12-13
Special Right Triangles:
Circles:
Area of a Circle:
2
Ar
π
=
Circumference of a Circle:
2Cr
π
=
A radius and tangent make a
right ∠
A central ∠ is double the
inscribed ∠
The Ultimate Formula Sheet for ACT Math ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC
360
x arc
circumference
=
and
sec
360 _ _
x tor
area o f circle
=
where x = central angle
Polygons: (for this section, n is the number of sides)
Area of a Rectangle:
A lw=
Area of a trapezoid:
12
1
()
2
b bh
+
Sum of the exterior angles: 360°
Sum of the interior angles:
180( 2)n −
One int. ∠ of a regular polygon:
180( 2)n
n
−
# of diagonals:
( 3)
2
nn−
(convex only)
Properties of Parallelograms:
1. Opp sides are ∥ and ≅
2. Opp ∠’ s are ≅
3. Consec ∠’s are supplementary
4. Each diagonal forms a pair of ≅∆’s
5. Diagonals bisect each other
If they are ≅ it is a rectangle
If they are ⊥ it is a rhombus
6.
Area base height= ×
Solids:
Volume of a Rectangular Prism (Box):
V lwh=
Surface Area of a Box:
2( )SA lw lh wh= ++
Volume of a Cylinder:
2
V rh
π
=
Surface Area of a Cylinder:
2
22
SA r rh
ππ
= +
Volume of a Sphere:
3
4
3
Vr
π
=
Volume of a Cone:
2
1
3
V rh
π
=
Volume of a Pyramid:
1
3
V lwh=
Trigonometry:
sin
opp
hyp
=
cos
adj
hyp
=
tan
opp
adj
=
1
csc( )
sin( )
x
x
=
1
sec( )
cos( )
x
x
=
1
cot( )
tan( )
x
x
=
360°=2π radians
sin
tan
cos
x
x
x
=
22
sin cos 1xx+=
sin( ) cos(90 )xx= −
Law of Sines:
sin sin sin
abc
ABC
= =
Law of Cosines:
2 22
2 cos( )
a b c bc A=+−
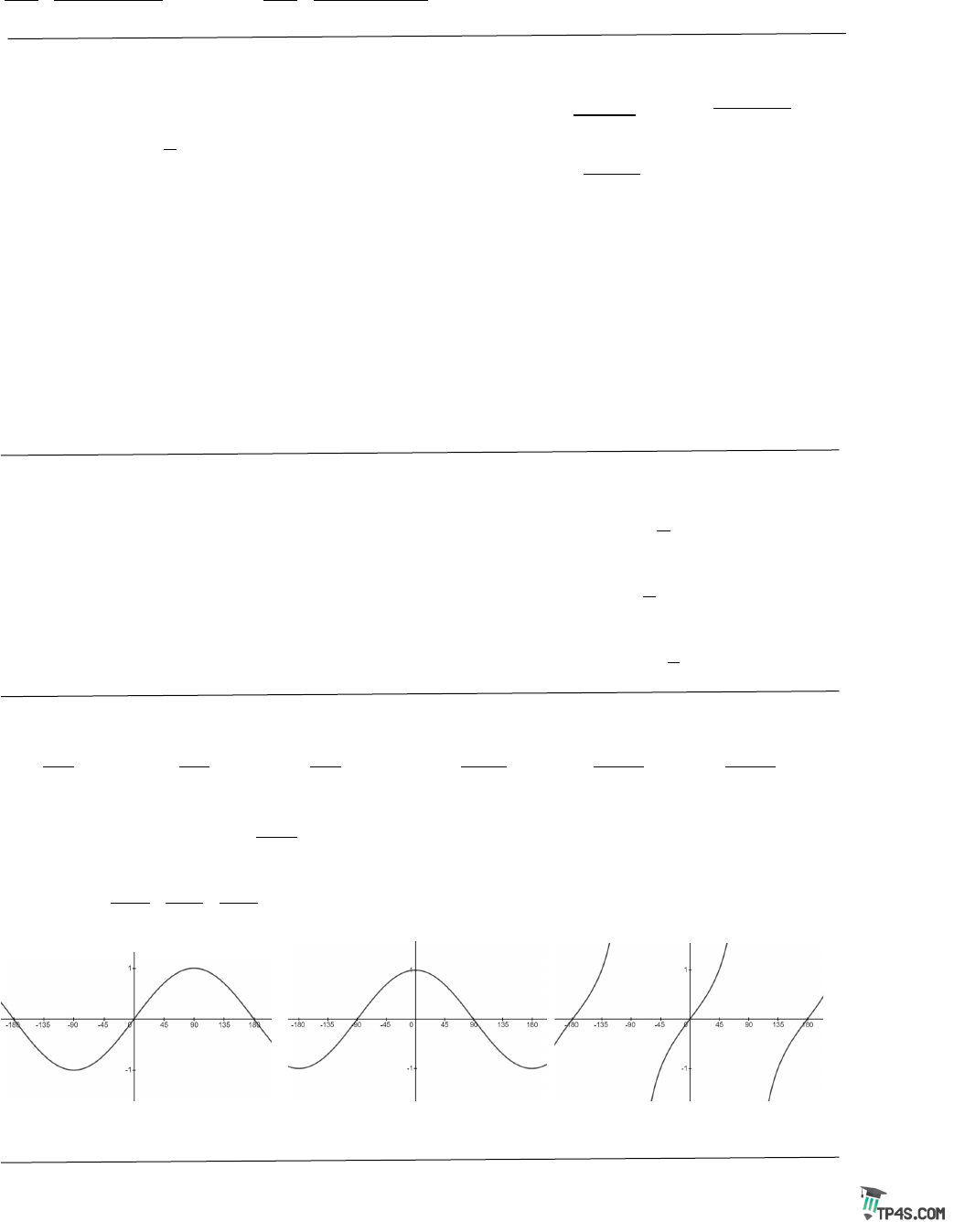
sin( )yx=
cos( )yx=
tan( )yx=

The Ultimate Formula Sheet for ACT Math ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC
If
sin( )y A Bx C D= −+
(also for cos, csc, and sec)
Amplitude:
A
Period:
2
B
π
Phase Shift:
C
B
Vertical Shift: D
If
tan( )y A Bx C D= −+
(also for cot)
Amplitude: none Period:
B
π
Phase Shift:
C
B
Vertical Shift: D
Sequences and Series: where
1
a
= first term, n = number of terms, d = common difference, r = common ratio
Arithmetic sequence:
1
( 1)
n
aa n d=+−
Sum of an arithmetic series:
( )
1
2
nn
n
S aa= +
Geometric sequence:
1
1
n
n
a ar
−
=
Sum of a geometric series:
1
( 1)
1
n
n
ar
S
r
−
=
−
Logarithms:
If
log
b
ax
=
, then
x
ba=
log
log
log
b
a
a
b
=
Vector Addition:
22
2 cos
a b a b ab
θ
+= + +
Matrix Multiplication: Only possible when columns of first = rows of second
A B E F AE BG AF BH
C D G H CE DG CF DH
++
×=
++
Determinant of
AB
AD BC
CD
= −
Conic Sections:
Circle:
2 22
( )( )xh yk r
− +− =
, where (h,k) is the center and r is the radius
Ellipse:
22
22
( )( )
1
xh yk
ab
−−
+=
where (h,k) is the center, 2a is the horizontal axis, and 2b is the vertical axis
Horizontal Ellipse:
2 22
abc= +
Vertical Ellipse:
2 22
bac= +
where c is the distance from center to focus
Horizontal Hyperbola:
22
22
( )( )
1
xh yk
ab
−−
−=
Vertical Hyperbola:
22
22
( )( )
1
yk xh
ab
−−
−=
